Abacavir
Product Quick Detail
- Minimum Order
- 1
- Packaging
- 25kg/drum
- Delivery
- 15 Days
Specifications
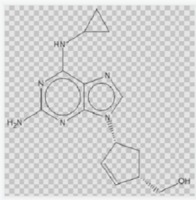
Abacavir
136470-78-5
C14H18N6O
The drug is extensively metabolized via stepwise phosphorylation to 5′-mono-, di-, and triphosphate. Abacavir is well absorbed (>75%) and penetrates the CNS. The drug can be taken without
regard to meals. The drug does not show any clinically significant drug–drug interactions. Abacavir has been reported to produce life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions. The major use of
abacavir appears to be in combination with other nucleoside RT inhibitors. A fixed-combination product has recently been approved by the U.S. FDA consisting of 300 mg of ABC, 150 mg of 3TC, and 300
mg of ZDV (Trizivar). The combination has been shown to be superior to other combinations in reducing viral load as well as to show improvement in CD4 cell count.
Treatment of 2,5-diamino-4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine (I) with (chloromethylene)dimethylammonium chloride yielded the dichloropyrimidine with both amino groups derivatized as amidines. Partial
hydrolysis with aqueous HCl in hot ethanol gave N-(2-amino-4,6-dichloro-pyrimidin-5-yl)-N,Ndimethylformamidene (II). Subseqent buffered hydrolysis at pH 3.2 yielded the
(2-amino-4,6-dichloro-pyrimididin-5-ylamino)acetaldehyde (III). Condensation chloropyrimidine (III) with (1S,4R)-4-amino-2-cyclopentene-1- methanol (IV) in the presence of triethylamine and NaOH
gave [2-amino-4- chloro-6-(4-hydroxymethyl-cyclopent-2-enylamino)pyrimidin-5-ylamino]- acetaldehyde (V). The correct enantiomer (IV) of racemic aminocyclopentene was obtained by resolution of
diastereomeric salts with D-dibenzoyltartaric acid. Cyclization of (V) to the corresponding purine was accomplished with refluxing triethyl orthoformate or diethoxymethyl acetate to give nucleoside
analogue [4-(2-amino-6-chloro-purin-9-yl)-cyclopent-2-enyl]methanol (VI). Displacement of chloride in the purine nucleus with cyclopropyl amine in refluxing butanol afforded abacavir. The structure
of obtained compound was confirmed by 1H NMR method and elemental analysis.
In practice it is usually used as sulfate salt.
In practice it is usually used as sulfate salt.
- Country: China (Mainland)
- Business Type: Hangzhou Huisheng Biotech Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd
- Market:The Middle East,Europea,Russia,and South America and US market
- Founded Year:2002
- Address:
- Contact:Tibi Teng