PVD COATING
Specifications
PVD COATING
Physical vapour deposition, just ar PVD coating, as we usually call it, refers to vacuum ion plating and vacuum sputter plating; Generally speaking, ncvm coating refers to vacuum evaporation
coating. The basic principle of PVD surface treatment is to vaporize the coating material under vacuum, and then deposit it evenly on the surface of the target part through electrons. The
advantages of PVD on plastic are: good adhesion of coating (good mechanical properties), strong winding ability (adjustable target position and electroplating path), good coating quality (dense,
uniform, high strength and long service life), simplified cleaning process (with cleaning function), and a wide range of plating materials (metal and non-metal can be plated).
Does PVD Coating Wear Off?
The wear resistance of white pvd plating system is different with different electroplating materials. For example, the CRN coating on the surface of bearings and cutting tools has strong wear
resistance and is not easy to wear off.
Is PVD Better Than Stainless Steel?
Aluminium PVD Physical Vapour Deposition is a surface treatment process. PVD surface treatment aims to improve or improve the performance and appearance of metal surfaces, and cannot be compared
with the performance of cheap CNC material.
Types Of PVD Coating on Plastic Parts
There are different types of pvd titanium coating sdn bhd that can be offered depending on the application requirements. Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Titanium Aluminum Nitride
(TiAlN), Titanium Boron Nitride (TiBN) are some examples of PVD coatings.
PVD Coating Advantages
Physical vapour deposition coatings offer the following benefits:
PVD surface treatment has high hardness (2400-4000 HV) (~ 80-90 HRc).
PVD physical vapour deposition is high abrasion resistance.
PVD metal coating is low friction coefficient (high surface lubricity)
Reduced tool heating due to low thermal conductivity of PVD physical vapor deposition.
Physical vapor deposition coating is well resistance to chemical environments
PVD metal finish can increase surface quality of the machined parts
Preventing the processed parts from adhering to the tool-mold surface
No change in dimensions due to PVD coating thickness at micron level
Decrease in tool cost per piece due to increased tool physical life
Decreasing in workbench downtime periods since tool change frequency are decreased
PVD surface treatment can obtain homogeneous coating thickness in each area
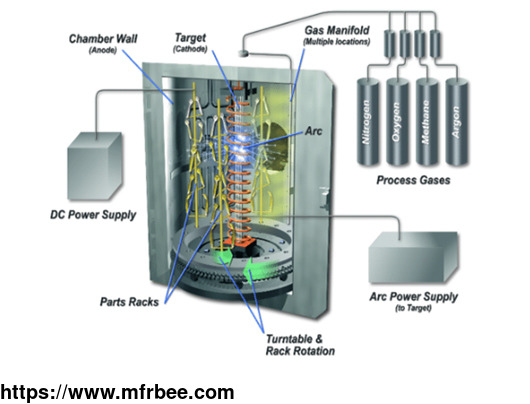
PVD Coating Technology
PVD coatings can be applied on components using different PVD technologies such as arc evaporation, magnetron sputtering to name a few. HEF specializes in plasma enhanced magnetron sputtering, CAM
(coating assisted by microwaves) and modified arc evaporation coating technologies. PVD coating technology is the most important one of the methods in which hard ceramic coatings can be
successfully applied on mold and tool surfaces. This PVD technology is based on the principle of ionic accumulation of materials under vacuum by being evaporated and/or sputtered on the surface, to
which the coating is to be applied.
PVD Coating Applications
PVD coating can be found in a broad range of products. For example, PVD surface treatment is frequently used in architecture. There is a wide range of PVD coating applications, which is why it is
commonly used in high-tech industries. Some of the industries and applications in which we have applied PVD physical vapor deposition coating include coating on composites for aerospace, titanium
on medical implants and surgical tools, gold thin film to replace plating for electronics, non-metal, chemical resistant oxides for semiconductor parts and hard ceramic coatings for industrial
tools.
PVD Coating Thickness
In general, PVD surface treatment is thin film and are in the range of 1 to 5 microns. For reference, 25 microns equals 0.001 inches. Red blood cells are around 8 microns in diameter, while human
hair is around 80 microns in diameter. Thus, PVD coatings are extremely thin-film coatings with thickness specification defined within this 1 to 5-micron range depending on the application
requirement.
PVD Coating Hardness
PVD physical vapor deposition coatings have a hardness value around 1500 – 4500 HV (Vickers) depending on the types of PVD coating offered. Vickers (HV) is a microhardness unit for measuring PVD
thin film coatings. For reference, 900 HV corresponds to 67 HRC (Rockwell C) hardness. Generally, carbon steels have a hardness range around 250 HV (25 HRC), nitrided or nickel and chrome plated
steels fall in the range of 600 HV to 1000 HV surface hardness. Thus, PVD coatings are extremely hard and hence, very durable and wear resistant.
Shenzhen Richconn Technology Co,. Ltd , as a China CNC machining oem factory, was established in 2012 and has two processing bases in Shenzhen and Dongguan, Guangdong, of which the Shenzhen base
covers an area of 5000 square meters and the Dongguan base covers an area of 3000 square meters.
- Country: China (Mainland)
- Business Type: Manufacturer
- Founded Year: 2003
- Address: 1212, Zehua building, intersection of Longhua Meilong road and donghuanyi Road, Songhe community, Longhua street, Longhua District, Shenzhen,GuangDong,China
- Contact: richconn cnc