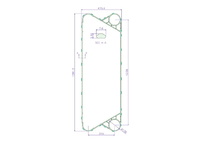
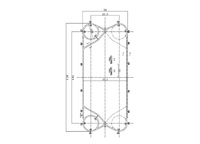
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Product Quick Detail
- FOB Price
- USD $5.00 / Piece
- Minimum Order
- 10
- Place Of Origin
- China
- Packaging
- N/A
- Delivery
- 1-15 workdays
Specifications
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are versatile and efficient devices that facilitate heat transfer between two or more fluids. Their unique design comprises a series of plates with gaskets, forming
channels for the fluids to flow through. These gaskets ensure a tight seal, preventing any cross-contamination between the fluids. The plates are specially designed with corrugations to increase
the heat transfer surface area and promote turbulence.
Types of Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Alfalaval Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
APV Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Tranter Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
GEA Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Kelvion Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Sondex Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
ITT Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
SWEP Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
VICARB Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Viex Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Viex Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
API-Schmidt Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
FUNKE Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
THERMOWAVE Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
HISAKA Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Mueller Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
FISCHER Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
SASAKURA Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
LHE Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
DHP Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
AGC Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Armstrong Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Cipriani Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
What Is the Difference Between a Gasketed and Welded Plate Heat Exchanger?
01
Sealing Method and Maintenance
The main difference lies in the sealing method and maintenance approach. Gasketed plate heat exchangers use gaskets to create a seal between the plates, allowing for easy maintenance and gasket
replacement. On the other hand, welded plate heat exchangers do not rely on gaskets but instead use welding to permanently join the plates together. This eliminates the need for gasket replacement
and simplifies maintenance. However, in case of any issues, welded plate heat exchangers may require more extensive repairs or replacements compared to gasketed heat exchangers.
02
Flexibility and Adaptability
Gasketed plate heat exchangers offer more flexibility in terms of plate arrangement and customization. The number and configuration of plates can be easily adjusted to accommodate different heat
transfer requirements. Gasketed plate heat exchangers also allow for handling various fluid types with different corrosive properties. In contrast, welded plate heat exchangers have a fixed plate
arrangement, and customization options are limited. They are generally suitable for specific applications with consistent operating conditions.
03
Pressure and Temperature Limitations
Welded plate heat exchangers are generally capable of handling higher pressure and temperature conditions compared to gasketed plate heat exchangers. The welded construction provides a robust and
secure seal, allowing for operation at elevated pressures and temperatures. Gasketed plate heat exchangers have limitations on pressure and temperature due to the reliance on gaskets for sealing.
Efficient Heat Transfer of Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers (GPHEs) with gasketed plate evaporator offer efficient heat transfer in a compact and space-saving design, surpassing the size and efficiency of traditional
shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Plate heat exchangers are specifically engineered to maximize heat transfer efficiency. The corrugated plates create a significantly larger surface area, enabling optimal heat transfer between
gases or liquids.
These heat exchangers feature a flexible design that simplifies service and maintenance procedures.
Advantages of gasketed plate heat exchangers include:
(1) Precise heat transfer: Achieves a closer approach temperature, facilitates true counter-current flow, and significantly reduces hold-up volume by 80-90%.
(2) Cost-effective operation: Offers low capital investment, reduced installation costs, and limited maintenance and operating expenses.
(3) Enhanced reliability: Minimizes fouling, stress, wear, and corrosion, resulting in improved reliability and prolonged operational lifespan.
(4) Environmentally conscious: Minimizes energy consumption while maximizing process effectiveness, contributing to lower environmental impact and reduced cleaning requirements.
(5) Expandable capacity: Allows for easy capacity expansion by adding or removing plates on the existing frame, providing flexibility for future growth and changing process demands.
Plate and gasket heat exchangers deliver efficient heat transfer, cost-effectiveness, reliability, environmental responsibility, and scalability, making them a preferred choice for various
industrial applications.
- Country: China (Mainland)
- Business Type: Manufacturer
- Address: Yard1, Hongye East Road, Daxing District, Beijing, China
- Contact: plateheatexchange com